Symptoms Common Causes And Treatment Of Eczema
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by dry, itchy, red, and inflamed patches of skin. Eczema can occur at any age, but it most commonly starts in infancy and childhood. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the symptoms, common causes, and treatment options available for managing eczema.
It's important to note that eczema symptoms can occur in cycles, with periods of flare-ups and remission. Flare-ups refer to periods of increased symptoms and irritation, while remission refers to periods when the symptoms subside or disappear temporarily.
Symptoms of Eczema;
Itchiness and Redness;
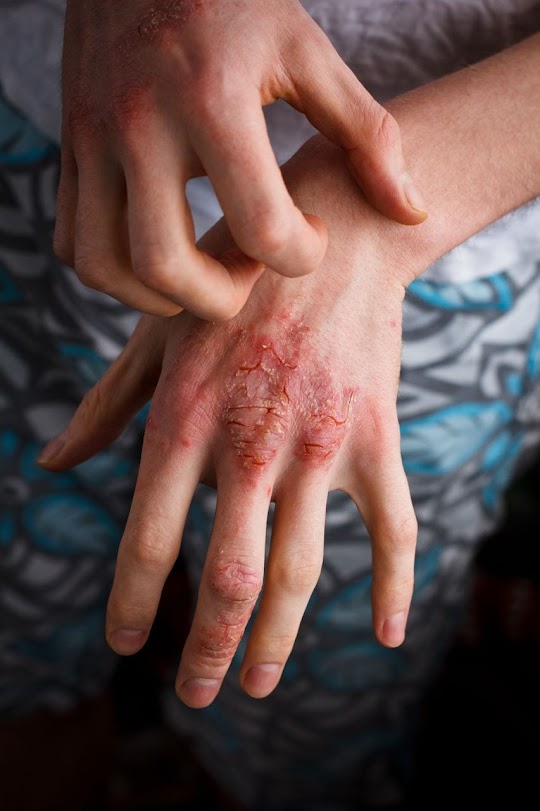
One of the hallmark symptoms of eczema is intense itching, which can be persistent and disruptive. Scratching the affected areas can lead to further inflammation, redness, and irritation of the skin.
Dry and Flaky Skin;
Eczema often causes the skin to become dry, rough, and scaly. The affected areas may appear cracked and may even bleed in severe cases. The skin's natural barrier function is compromised, resulting in increased water loss and dryness.
Inflammation and Swelling;
The affected skin patches are typically red, inflamed, and swollen. Inflammation is a result of the immune system reacting to triggers and releasing inflammatory mediators, leading to an exaggerated immune response in the skin.
Cracking and Oozing;
In some cases, eczema can cause the skin to crack, especially in areas that bend or flex frequently, such as the elbows and knees. These cracks can be painful and may ooze clear or yellow fluid, forming crusts or scales.
Secondary Infections;
Due to the compromised skin barrier and constant scratching, eczema-prone skin is susceptible to bacterial, viral, or fungal infections. Common infections include impetigo (bacterial), herpes simplex (viral), and candidiasis (fungal). These infections can worsen eczema symptoms and require medical intervention.
Thickened Skin (Lichenification);
Chronic or recurrent scratching and rubbing can lead to thickening of the affected skin, a condition known as lichenification. The skin becomes leathery and more resistant to treatment, making it even more challenging to manage eczema.
Sleep Disturbances;
The persistent itchiness and discomfort associated with eczema can significantly impact sleep patterns, leading to sleep disturbances and daytime fatigue. Itchiness tends to worsen at night, making it difficult for individuals with eczema to get a good night's sleep.
MORE HUBS;
Common Causes of Eczema;
Genetic Factors;
There is a strong genetic component to eczema. People with a family history of eczema, allergies, or asthma are more likely to develop eczema themselves. Certain gene variations have been linked to an increased susceptibility to eczema, affecting the skin's ability to retain moisture and maintain a healthy barrier function.
Environmental Triggers;
Various environmental factors can trigger or exacerbate eczema symptoms. Everyday substances like soaps, detergents, shampoos, fragrances, and certain fabrics can irritate the skin and trigger eczema flare-ups. Common allergens, such as dust mites, pet dander, pollen, mold, and certain foods, can act as triggers for eczema symptoms in susceptible individuals. Extreme temperatures, low humidity, and excessive sweating can all contribute to dryness and worsen eczema symptoms. Certain bacteria, viruses, and fungi can infect the skin and aggravate eczema. Staphylococcus aureus is a common bacterium found on the skin of people with eczema and can contribute to inflammation and infection.
Exposure to certain chemicals, such as solvents, cleaning agents, and industrial chemicals, can trigger or worsen eczema symptoms in some individuals.
Immune System Dysfunction;
Eczema is associated with an overactive immune response in the skin. The immune system's abnormal reaction to triggers leads to inflammation and the release of inflammatory substances, contributing to the development of eczema symptoms.
Allergies and Sensitivities;
Eczema and allergies often coexist, indicating a shared underlying immune mechanism. Some individuals with eczema may have allergic reactions to certain foods, inhalants, or contact allergens, which can trigger or worsen their eczema symptoms.
Stress and Emotional Factors;
Emotional stress and psychological factors can influence the severity and frequency of eczema flare-ups. Stress and anxiety can weaken the immune system and make the skin more sensitive and reactive, leading to eczema exacerbations.

Prevention and Proactive Measures for Eczema
While eczema cannot be completely prevented, there are several proactive measures and lifestyle changes that can help reduce the frequency and severity of flare-ups. By following these preventive strategies, individuals with eczema can effectively manage their condition and improve their quality of life. Here are some key prevention strategies:
Skin Protection:
Use emollients and moisturizers to keep the skin hydrated and prevent dryness. Apply moisturizer immediately after bathing to lock in moisture.Use mild, fragrance-free, and hypoallergenic cleansers that do not strip the skin of its natural oils.
Wear protective gloves while handling household chemicals, detergents, and other potential irritants.
Choose gentle fabrics: Opt for soft, breathable fabrics like cotton and avoid rough, scratchy materials that can aggravate eczema-prone skin.
Take regular baths or showers with lukewarm water and avoid prolonged exposure to hot water, as it can dry out the skin.
Allergen Avoidance;
Keep a diary to track potential triggers and identify substances that worsen your eczema symptoms. Common triggers include certain foods, dust mites, pet dander, pollen, mold, and specific chemicals. Take steps to avoid or minimize exposure to these triggers.
Maintain a clean environment: Regularly clean your living space to reduce dust, allergens, and potential irritants. Use hypoallergenic bedding and vacuum with a HEPA filter.
Manage pet allergies: If you have allergies to pet dander, consider limiting exposure to pets or creating pet-free zones within your home.
Healthy Lifestyle Habits;
Eat a nutritious diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Some individuals may find that certain foods trigger their eczema symptoms, so it's important to identify and avoid these potential triggers.
Drink an adequate amount of water to keep your skin hydrated from within.
Practice stress-reducing techniques like meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga, or engaging in hobbies to manage stress levels. Stress can worsen eczema symptoms, so finding healthy coping mechanisms is important.
Keep nails short and consider wearing cotton gloves at night to prevent scratching during sleep. Scratching can further damage the skin and lead to infections.
Engage in regular physical activity to improve overall health and boost your immune system. However, be mindful of excessive sweating, which can trigger eczema flare-ups. Shower and moisturize promptly after exercise.
Moisturize and Protect Babies and Children;
Use fragrance-free and hypoallergenic skincare products specifically formulated for babies and children.
Keep their skin moisturized with gentle, non-irritating emollients or creams.
Dress them in loose-fitting, breathable clothing made of natural fabrics.
Be cautious with introducing new foods, and consult a pediatrician if you suspect any food allergies.

Treatment Options for Eczema
The treatment of eczema aims to manage symptoms, reduce inflammation, relieve itching, and improve the skin's overall health. The treatment approach may vary depending on the severity of the condition, age of the individual, and other factors. Here are some common treatment options for eczema:
Moisturizers;
Regular use of emollients and moisturizers to keep the skin hydrated and prevent dryness.
Topical Corticosteroids;
Prescription creams or ointments to reduce inflammation and itching.
Topical Immunomodulators;
Non-steroidal creams that modulate the immune response and reduce inflammation.
Systemic Medications;
Oral or injectable medications prescribed for severe cases.
Antihistamines;
Oral or topical medications to alleviate itching and improve sleep during flare-ups.
Phototherapy;
Controlled exposure to ultraviolet light under medical supervision to reduce inflammation.
Wet Wrap Therapy;
Applying emollients and wrapping the skin with wet bandages or clothing to enhance hydration and effectiveness of medications.
Trigger Avoidance;
Identifying and avoiding triggers that worsen eczema symptoms, such as certain foods, irritants, or allergens.
Complementary Therapies;
Some individuals find relief through acupuncture, herbal remedies, and relaxation techniques, but consult a healthcare professional before trying them.
Counseling and Support;
Seeking emotional support and stress management techniques to cope with the impact of eczema on mental health.
It's crucial to work closely with a healthcare professional, such as a dermatologist, to develop an individualized treatment plan tailored to your specific needs and condition. They can guide you in choosing the most appropriate treatments and help monitor your progress to achieve optimal control of eczema symptoms.
Conclusion;
Eczema is a chronic skin condition characterized by symptoms like itchiness, redness, dryness, and inflammation. While it cannot be completely cured, effective management strategies can help control symptoms, reduce flare-ups, and improve overall quality of life.
Understanding the symptoms and common causes of eczema is essential for proper diagnosis and treatment. Identifying triggers and taking preventive measures can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of flare-ups. This includes protecting the skin, avoiding irritants and allergens, practicing good hygiene, and managing stress levels.
Treatment options for eczema range from moisturizers and topical corticosteroids to systemic medications and phototherapy. The choice of treatment depends on the severity of the condition and individual factors. It's important to work closely with a healthcare professional to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses your specific needs and goals.
Additionally, adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, proper hydration, and stress management techniques, can contribute to better eczema management. Seeking emotional support and counseling can also help individuals cope with the emotional impact of eczema and maintain a positive outlook.
While living with eczema can be challenging, with the right strategies and support, individuals can effectively manage their symptoms, minimize flare-ups, and enjoy a better quality of life. By staying informed, following a comprehensive treatment plan, and making necessary lifestyle adjustments, those affected by eczema can find relief and regain control over their skin health.







Comments
Post a Comment